Alexa privacy: What you need to know

Every time you ask Alexa to play a song, set a reminder, or check the weather, your voice is recorded and sent to Amazon’s servers for processing. Those recordings can include background sounds, conversations, and other data you might not realize are being captured.
Understanding how Alexa handles that information is key to protecting your privacy. This guide explores what happens to your recordings after they’re processed, how that data fits into Amazon’s broader ecosystem, and what you can do to stay in control.
How Alexa handles your voice data
Alexa’s ability to respond accurately relies on analyzing and storing snippets of your voice data. Amazon uses these snippets to train its speech-recognition systems and improve how Alexa understands different accents and phrasing. Additionally, a small sample of your voice could be reviewed by humans to check whether Alexa interpreted requests correctly.
While this process helps refine Alexa’s performance, it also means your voice interactions are retained on Amazon’s servers, which is an important factor for anyone concerned about their data privacy.
How Alexa listens for commands
Alexa’s microphones are always active to detect a wake word, but you can manually mute them at any time.
When active, Alexa devices stay in standby mode, monitoring ambient sound locally to detect their wake word. Only after that word is recognized does the device begin recording and send your request to Amazon’s servers to process the request.
Occasionally, Alexa can activate unintentionally if background noise sounds similar to the wake word. When this happens, a brief recording is sent to the cloud for verification, helping Amazon’s systems refine wake-word accuracy over time. Users can review, delete, or manage these clips in their Alexa privacy settings.
How to protect your privacy with Alexa
When an Alexa device is first set up, its default settings allow voice recordings to be stored in your Amazon account. These recordings are retained on Amazon’s servers until you manually delete them or set up an automatic deletion schedule. Each command, whether intentional or triggered by mistake, becomes part of that stored history unless removed by the user.
Adjusting your privacy settings
Adjusting your privacy settings helps reduce how much data accumulates over time. It’s a straightforward way to keep Alexa functional while ensuring your personal information remains under your control.
Automatically delete your data
Setting recordings to delete automatically, or stopping them from being saved at all, reduces how much personal information remains stored in Amazon’s cloud.
Follow this simple guide on how to delete Alexa recordings to review and remove stored voice data from all your devices.
Evaluating apps and skills access
Alexa’s skills work much like apps on a smartphone; they expand what the device can do, but many request access to your personal data. Over time, it’s easy to lose track of which ones you’ve enabled and what information they can use.
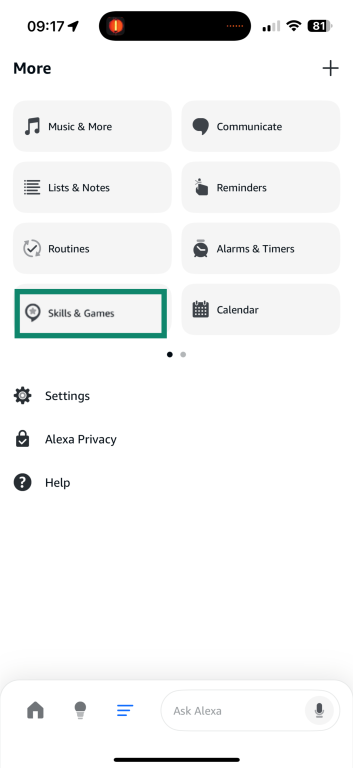
To review your active skills:
- From the menu, select Skills & Games to manage your installed Alexa skills.
- Tap Your Skills. This shows all the Alexa skills currently enabled on your account.
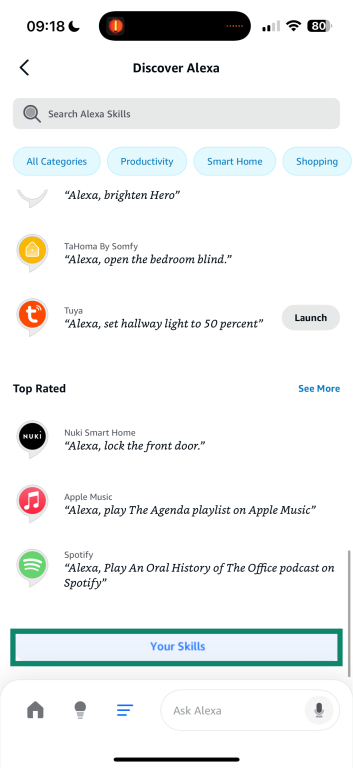
- Select a skill to view its details. Tap any skill, such as “Ring,” and tap Settings to review what data the skill can access, or Disable Skill to remove it completely.

If a skill no longer serves a purpose or requires access you’re not comfortable with, you can disable it directly from this screen.
Granting skill permissions
Some skills also need access to certain data, for example, your address for delivery updates or your calendar to schedule reminders. While these permissions can make Alexa more useful, they also increase how much personal information you share.
To manage skill permissions:
- From the Alexa Privacy menu, tap Manage skill permissions and ad preferences.
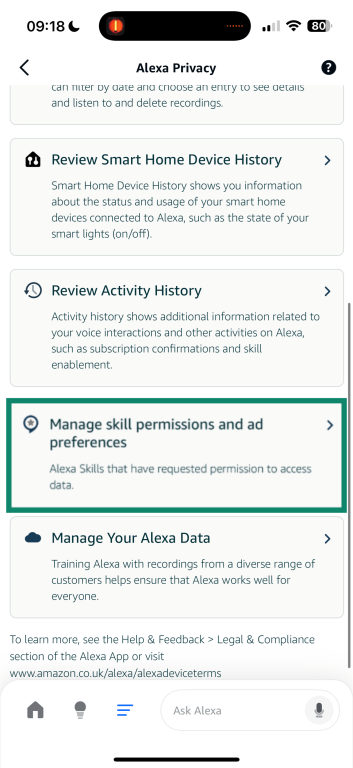
- Review the list of data types (such as location, contacts, or notifications), and toggle off any permissions you don’t want to share.
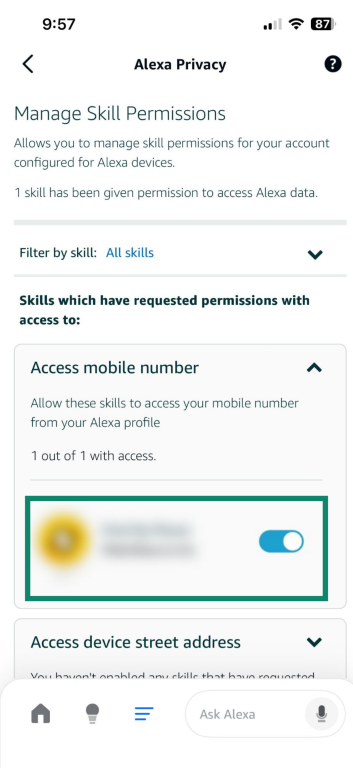
Disabling permissions may limit certain functions of skills, for example, if you don’t allow access to your calendar, Alexa may not be able to add something to your schedule.
Alexa and cybersecurity: How safe are smart assistants
Alexa’s capabilities mean that it can become the center of an entire smart home. If its security is weak, other devices can become easier targets, too. Understanding how Alexa fits into your digital ecosystem is the first step to keeping your connected home safe.
Common vulnerabilities in smart devices
A smart home network is only as secure as its least protected device. While Alexa devices themselves haven’t experienced any major security incidents as of November 2025, they rely on the same Wi-Fi networks and connected services as other smart gadgets. When other devices on the same network have weaker security measures, it can increase overall exposure to potential threats.
- Weak or unchanged passwords: Some smart devices still use factory-set credentials or simple passwords. If these aren’t updated, they can give intruders easy access to your network.
- Outdated firmware: Not all devices receive regular updates or security patches. When manufacturers stop supporting older models, known flaws may remain open to exploitation.
- Insecure connection features: Protocols like Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) simplify setup but can also open unintended pathways into your network. Without careful configuration, these shortcuts can be used to bypass security controls.
Tips to secure your smart home network
Keeping your connected home safe means protecting the basics: your router, your passwords, and how your devices share the same network. A few small adjustments can make a big difference in keeping intruders out.
- Strengthen your router: Your Wi-Fi router is the front door to your home network. Change the default login details and use strong, unique passwords for both the router and your Wi-Fi. Check that it uses the latest encryption standard, such as Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 (WPA2) or WPA3, to keep your connection secure. WPA3 offers stronger protection if your devices support it, but WPA2 remains a solid option.
- Use a separate network for smart devices: Create a guest or secondary network for devices like Alexa, smart plugs, or cameras. This separation limits access if one device is compromised and keeps your personal information on laptops and phones protected.
- Keep everything updated: Install firmware updates for your router and smart devices as soon as they’re available. Updates often fix critical security flaws. If a device stops receiving support from the manufacturer, it’s safer to replace or retire it.
- Turn off unused features: Options like remote access or voice purchasing make devices more convenient but can also expose them to unnecessary risk. Disable any features you don’t use regularly.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA): Add an extra layer of protection by turning on 2FA for your Amazon and smart-device accounts. It ensures that even if someone guesses your password, they can’t sign in without the second verification step from your phone.
Can a VPN protect you from Alexa privacy risks?
A virtual private network (VPN) encrypts your internet traffic and hides it from anyone trying to monitor your connection. However, Alexa sends most of its data, like voice recordings and usage information, directly to Amazon’s servers. A VPN can’t change how that data is handled, but it does help secure your home network and reduce exposure to other types of online tracking.
Here’s how it strengthens your overall privacy:
- Encrypting your network traffic: A VPN helps secure the connection between your devices and the internet, scrambling the data so your internet service provider (ISP) or anyone else on the network is less likely to read it.
- Masking your IP address: Instead of your real IP address, websites and services only see the VPN server’s address. This helps protect your location and prevents activity from being tied back to your home network.
- Reducing attack risks: When installed on your router, a VPN adds an extra layer of protection against attackers who might target weak smart devices to access the rest of your network. Even if data is intercepted, encryption makes it unreadable.
Alternatives to Alexa
For users who want to explore other smart assistants, there are several options that balance convenience and privacy in different ways. Each has its own approach to data handling and its own trade-offs.
Apple HomePod (Siri)
Apple’s smart speakers process many Siri requests directly on the device, which can reduce the amount of data sent to the cloud. When the cloud is used, voice recordings are not stored unless the user opts in, and any saved requests are separated from personal identity using random identifiers. Still, transcripts of your interactions and related metadata, like request type, device specs, or approximate location, can be retained for analysis.
Google Nest (Google Assistant)
Google has introduced stronger privacy controls over time. By default, Nest devices don’t retain audio recordings unless you choose to save them to improve speech recognition, and users can set auto-delete periods to clear their activity. Still, Google Assistant, like other cloud-based systems, processes most requests on company servers, meaning some level of data use remains necessary for functionality.
Local and open-source options
For users who prefer to keep everything offline, open-source systems such as Home Assistant (Assist) or Mycroft Mark II handle all processing locally rather than in the cloud. These tools offer greater transparency and control, but setup and maintenance can be more technical, and features are often more limited compared to commercial products.
FAQ: Common questions about Alexa privacy
What are the privacy concerns with Alexa?
Alexa records and stores short voice clips and timestamps every time you speak, building a profile of your habits over time. Unless you opt out, some recordings may also be manually reviewed to improve Alexa’s accuracy. Occasional false activations can also capture parts of private conversations.
How to keep Alexa private?
You can improve privacy by adjusting your Alexa privacy settings. Set recordings to delete automatically, stop saving new ones, and regularly review which apps and skills have permissions to access your data.
Can Alexa listen in on private conversations?
Alexa only records once it detects its wake word, but it can mishear and activate by accident. When that happens, short clips may be sent to Amazon’s servers, sometimes including private chatter.
What should I do if Alexa seems to be always listening?
If Alexa lights up unexpectedly, use voice deletion to remove recent clips or mute the microphone for peace of mind. You can also review stored recordings in the app and delete them manually. These quick actions stop Alexa from saving conversations you didn’t mean to share.
Can Alexa be hacked remotely?
It’s technically possible, but there haven’t been any reports of widespread hacking as of November 2025. In 2020, a potential avenue of attack was reported by the cyber threat intelligence agency, Check Point Research, and Amazon acted quickly to resolve the issue.
Can a VPN prevent Alexa from tracking me?
A VPN can’t block data that Alexa sends to Amazon’s cloud, but it does protect your network from outsiders. It encrypts your traffic so internet service providers (ISPs) and third parties can’t monitor connected devices or infer what you’re doing online.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN