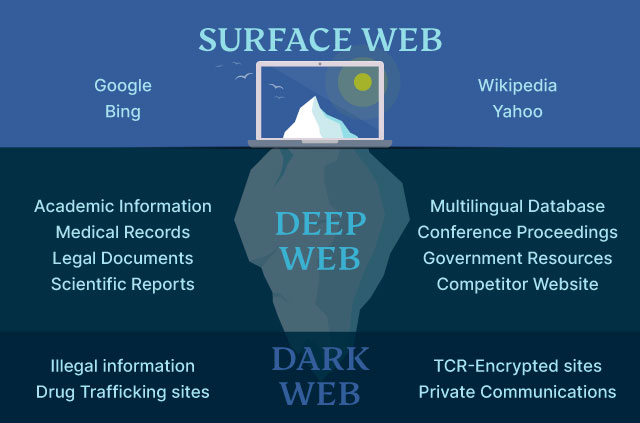
The difference between deep web and dark web, in short:
- Deep web: The part of the internet not indexed by search engines. Includes content like personal email accounts, private databases, and subscription-based services.
- Dark web: A small portion of the deep web that requires specific software (like Tor) to access. Often associated with illegal activities but also used for secure, anonymous communication.
The dark web and the deep web are often used interchangeably, but they’re two distinct concepts. In short, the major difference between them is that the deep web contains internet content you can’t find through search engines, while the dark web is a hidden network that requires a special browser to access.
You use the deep web daily when you check your email or shop online, but you’ll need the Tor Browser to use the dark web.
In this article, we’ll explain both the deep web and the dark web, the differences between the two, and some associated developments.
Jump to…
What is the deep web?
What is the dark web?
What is the difference between the deep web and the dark web?
Are the dark web and the deep web illegal?
Risks of accessing dark web and deep web
Benefits of using the dark web?
How to access the deep web safely
How to access the dark web safely
What is the deep web?
The deep web is the part of the internet you can’t access through search engines like Google and Bing. Also referred to as “non-indexed” content, it’s any content hidden behind some kind of access control such as a log-in or code word. Ever wonder how big the deep web is? It contains 7,500 terabytes of information, compared to only 19 terabytes of information in the “surface” web. To look at it differently, it makes up between 90% and 95% of the internet.
Deep web examples
Guess what? You’re on the deep web a lot more than you think! For instance, your Gmail inbox and your Google Drive are part of the deep web because they don’t exist as publicly accessible domains. Other examples include your bank account page and the settings page of your social media account, the admin page of your blog, and some academic journals. These websites exist in directories that Google (and other search engines) are barred from crawling.
Other examples of deep web content are:
- Private databases: Information in company intranets, academic databases, and government resources not accessible to the general public.
- Subscription services: Content behind paywalls like news sites, streaming services, and online courses.
- Personal information: User-specific content such as emails, online banking accounts, and health records.
- Unindexed websites: Pages not indexed by search engines for various reasons, such as being behind a login or having a no-index meta tag.
- Confidential corporate data: Internal communications, confidential reports, and proprietary data within a company’s private network.
What is the dark web?
The dark web, or the darknet, is a small subset of the deep web. It’s a hidden collective of sites that you can only access through a special browser. Since all activity on the dark web is anonymous by default, it is where the murkiest online transactions take place. A study by researchers at King’s College London that examined the contents of over 2,700 darknet sites found that approximately 60% of them hosted illicit content. With that said, legitimate websites also exist on the dark web.
To access the dark web, you’ll need special search engines like Candle, Not Evil, and SearX, all of which require a specialized browser like Tor to work. On the dark web, neither users nor web administrators reveal themselves to each other, including their identity or their location. Hence, it’s very hard to shut down dark web servers or place geo-restrictions on users.
Read more: Best dark web search engines
Dark web examples
The dark web hosts all kinds of illegal activities, many of which are the buying and selling of firearms, drugs, counterfeit money, fake passports, and stolen accounts.
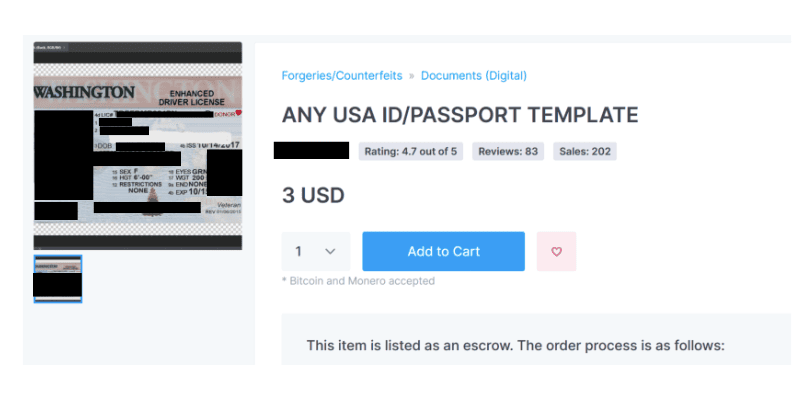
The Silk Road was perhaps one of the most well-known examples of an illegal marketplace in the darknet. It was shut down in 201, but not before it showed the world how easy it was to buy illegal drugs, counterfeit documents, and other questionable items online.
In fact, it can be argued that the closure of Silk Road and the subsequent arrest and conviction of Ross Ulbricht, its founder, only heightened interest in darknets and their illegal wares. Sociologist Isak Ladegaard, who built an algorithm to monitor sales data on Silk Road-type marketplaces, declared that all the media coverage boosted people’s awareness of the existence of the dark web. As a result, trading actually went up.
But the dark web isn’t only associated with illegal activity. Whistleblowers, journalists, and activists frequently log on to the dark web in order to stay anonymous and spread the results of their research. WikiLeaks, for example, hosts a site on the dark web. Even Facebook, DuckDuckGo, and ExpressVPN have websites on the dark web.
Other examples of dark web content include:
- Anonymous communication: Platforms like Tor and I2P enable private communication channels, often used by journalists, activists, and whistleblowers.
- Black marketplaces: Websites for buying and selling illegal goods and services, such as drugs, weapons, and counterfeit items.
- Hacking forums: Communities where hackers exchange information, tools, and services, often involving cybercrime activities.
- Illegal content: Sites hosting illegal content.
- Cryptocurrency transactions: Use of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin to facilitate anonymous financial transactions.
Do you know how much your information is really worth on the dark web? Take our quiz to find out.
Five key differences between the dark web and the deep web?
As we mentioned at the start of this article, the dark web and the deep web are often conflated. The easiest way to understand the difference is that not all deep web is the dark web but all dark web is the deep web.
Here’s a quick dive into their differences in terms of various aspects:
| The deep web | The dark web | |
| Scope | Much broader scope than the dark web, covering a range of content that is not accessible by web search engines. | A subnet of the deep web, the dark web is much narrower in scope. |
| Operations | Doesn’t require a special browser or unique protocols. Most of its content is password-protected. | Can’t be accessed without a special browser called Tor, which is designed to maintain user anonymity. |
| Size | 400 to 500 times larger than the surface web. | Only 0.01% of the deep web and 5% of the total internet. |
| Applications | Intranets used by institutions or companies. Free services like Gmail, and subscription-based services like Netflix and Amazon. | Used mostly for criminal activity, whistleblowing and expressions of dissent. |
| Security | Attacks are focused on your login credentials, in the form of various types of scams like phishing emails and fake login prompts. | The risk comes in when you download illegal materials which contain viruses or malware, like trojans, worms, or keyloggers. |
Ready for a deep dive? We’ve elaborated on their differences in greater detail below.
The deep web has a broader scope
The deep web has a much broader scope than the dark web. It covers a range of content that is not accessible by web search engines like Google, Safari, or DuckDuckGo. It’s anything that is password-protected, including emails, chat conversations, and private posts of social media accounts. The dark web, which is a subset of the deep web, is much narrower in scope.
Accessing the dark web requires a specific browser
Accessing the deep web doesn’t require a special browser or unique protocols. The dark web, however, can only be accessed through the Tor browser. The encrypted nature of the browser means everyone trying to access the dark web remains anonymous by default. What’s more, URLs on the dark web are starkly different from regular web addresses.
All sites on the dark web end with “.onion,” as opposed to “.com” or “.org” commonly seen on the surface web. That’s a deliberate ploy so that only browsers with specific proxies are allowed to access those sites. It’s also very difficult to remember the URLs of sites on the dark web, which is another way to maintain their anonymity.
While Tor is the most popular way of accessing dark nets, the Invisible Internet Project (I2P) is another decentralized anonymizing project that deploys similar principles to Tor. Effectively a self-contained internet, I2P allows users to send emails, write blogs, and chat anonymously much like they would on the regular web.
The dark web is much smaller than you think
Let’s put some numbers into perspective. The deep web is approximately 400 to 500 times greater than the surface web. The dark web is only a small fraction of the deep web—constituting only 0.01% of it and 5% of the total internet.
The deep web has more applications than the dark web
The deep web is much more widely applicable to internet users than the dark web. Intranets used by companies or schools and paid or free online services are all part of the deep web. In other words, you’re on the deep web when you’re going through your emails, checking your balance on the bank account page, or managing your Dropbox folders.
On the other hand, the dark web welcomes more distinct groups of users, like criminals, whistleblowers, or political dissidents, who leverage off the anonymity the dark web provides. With that said, any regular internet user can visit the dark web, which is not illegal to use.
The deep web is generally safer and more secure than the dark web
The deep web is generally safe and secure to use; owners of private websites or services are responsible for maintaining their security. That said, cybercriminals increasingly target this part of the internet because of the lucrative personal data lying within. That’s why basic online hygiene has become critical to protecting yourself online. Read on to find out how to access the deep web safely.
It’s generally safe if you are just browsing on the dark web. The danger comes in when you download illegal materials that contain viruses or malware, like trojans, worms, or keyloggers.
Are the dark web and the deep web illegal?
Using the Tor browser or trying to access a non-indexed page is perfectly legal. Just because a page cannot be accessed by search engines doesn’t mean it’s trying to promote illicit activity. Similarly, logging on to the Tor browser in order to browse the dark web doesn’t mean you’re breaking any laws.
What is illegal, however, is anything that would be illegal online or offline, such as buying illegal items like drugs or counterfeit documents, organizing illegal services like hacking, or accessing illegal content.
What are the risks of accessing the dark web and deep web
The deep web is where you constantly supply your login credentials to access a range of online services, like email, e-banking, and social media. It also attracts a lot of attention from attackers who want to get a hold of your personal data by running all kinds of scams behind phishing emails, LinkedIn messages, or fake login prompts.
The risks of the dark web come when you aren’t careful with what you access. You can fall prey to scams and give away your personal data. Worse, you can stumble on illegal activity or disturbing content.
Malware and viruses
Browsing the dark web can expose your device to malicious software. Malware, including viruses, trojans, and ransomware, can infiltrate your system, leading to data theft, loss, or damage.
Scams and phishing
Scammers often target users on the dark web, employing phishing tactics to steal personal information and financial details. These scams can result in significant financial loss and identity theft.
Cybersecurity issues
Accessing the dark web without proper precautions can make you vulnerable to cyber attacks. Hackers may exploit weaknesses in your security setup, leading to unauthorized access to your data and devices.
Exposure to harmful and illegal activities
The dark web hosts a range of illegal activities and content. Encountering or inadvertently engaging with this material can have serious legal and ethical repercussions, putting you at risk of legal action or psychological harm.
What are the benefits of using the dark web?
Despite its reputation, the dark web can also be a very powerful tool and can offer benefits. Some of them are:
- Enhanced privacy and anonymity: The dark web allows users to communicate and browse without revealing their identities, which is crucial for journalists, activists, and whistleblowers in oppressive regimes.
- Access to information: In regions where the internet is heavily censored, the dark web can provide access to uncensored information and resources.
- Secure communication: It offers secure platforms for sensitive communications, ensuring confidentiality.
- Innovative marketplaces: Some dark web marketplaces focus on legitimate goods and services, offering niche products and innovative services not found on the surface web.
How to access the deep web safely
Accessing the deep web is generally safe. A lot of it comes down to practicing basic online hygiene practices:
- Use a VPN: A VPN download can help maintain your privacy and increase your anonymity on the internet by obfuscating your IP address and routing your internet traffic through an encrypted tunnel. Hackers, governments, and your ISP cannot eavesdrop on your online activity, even if it’s on unsecured networks such as public Wi-Fi.
- Adhere to safe password practices: Always create unique passwords for each account and store your passwords in a secure place. All these sound like a hassle to you? A password manager will come in handy.
Here are a few more ways to access the deep web safely.
How to access the dark web safely
Like other parts of the internet, the dark web has scams and third parties trying to steal your data through phishing. Here are some ways to keep yourself safe when navigating it.
- Download the Tor browser from the official website: The Tor browser is still the easiest and safest way to access the dark web. Knowing this, potential attackers will make you download their bogus version containing malware or viruses that can infect your device. Make sure you’ll get the official version of Tor at torproject.org.
- Use a VPN: The government and your internet service provider can’t track your activity on the Tor browser, but they will know that you’re on the Tor network. To prevent this, use a VPN. It deflects unwarranted suspicion by encrypting your web traffic and makes your Tor-encrypted data even harder to crack.
- Take security precautions: Use a burner email address, encrypt your messages with PGP, and disable Javascript on your Tor browser. Avoid clicking on random onion URLs and make sure to verify a site’s authenticity before logging on. Some useful sources on Reddit to verify onion sites include /r/deepweb, /r/onions, and /r/Tor.
FAQ: About deep web and dark web
What are the best browsers for the deep web and the dark web?
Regular internet browsers like Google Chrome or Safari should suffice for browsing the deep web. But Tor is the best option for both the deep web and the dark web as it instantly deletes cookies, browsing history, and other data for you. No matter what browsers you choose to use, the best practice is to always use a VPN, which gives you an additional layer of privacy and security.
Is the deep web safer than the dark web?
In theory, the deep web is safer than the dark web. The deep web is just that part of the internet that is not indexed by search engines. The dark web is dubbed as a hotbed for illegal activity. That said, if you’re just browsing on the dark web, it should be as equally safe as doing so on the deep web.
Can the police track you on the dark web?
Yes, the police can still track you on the dark web if they need to, although it’s extremely hard to do so. The Tor browser you use to access the dark web can mask your identity and location. The average user won’t be able to identify you on the dark web, but the authorities can still track you down with high-level technologies. That is, if you give them a good enough reason to.
Which is deeper–the deep web or the dark web?
The dark web is deeper than the deep web. Its nature as a hub for anonymity means it hides away from public access and scrutiny.
Who created the dark web?
The dark web is the product of the U.S. government attempting to build communication networks for military and self-defense purposes.
The Tor browser was designed to facilitate anonymous message sharing among U.S. spies spread across the world, and was made publicly available software in the early 2000s.
While the original aim of the dark web was to facilitate secret communication, the network’s anonymous nature also encouraged illegal activity. Helped by the launch of Bitcoin in 2009, the dark web quickly became a platform for criminals to source and deliver illegal items.
What is the best dark web vpn?
ExpressVPN is your best bet for browsing the dark web. It gives you an additional layer of encryption and anonymity—backed by a strict no-log policy. Try it yourself and get a full refund within 30 days if you’re not satisfied.

Mask your IP address with a VPN
30-day money-back guarantee























Comments
The internet has a profound effect on humanity, which is something I like to think about.
Vera level